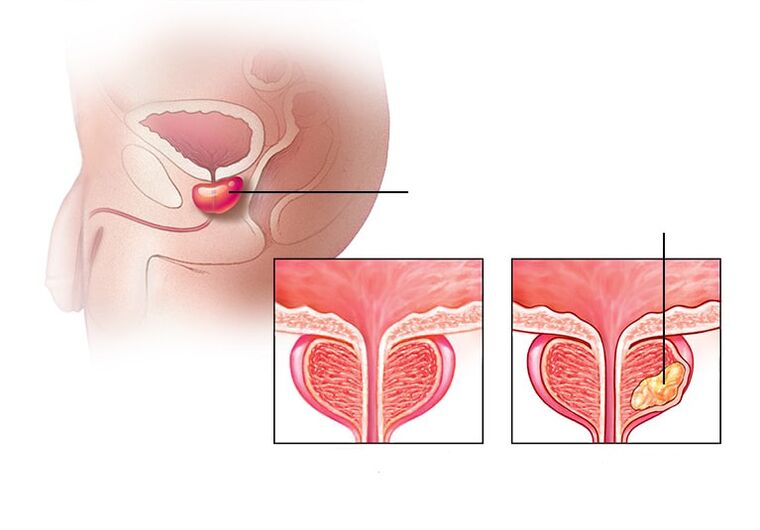
Prostatitis is an inflammatory process associated with inflammation of the prostate (prostate) in men. The disease is most common in men over the age of 30. The disorder causes pain in the lower back, perineum, or pelvic area, along with disturbances in the normal process of urination, and in severe cases, erectile dysfunction and serious problems with partners.
In about a quarter of couples suffering from infertility, it is the male factor that prevents conception. Male infertility is a violation of sperm quality and its quantitative content in ejaculate.
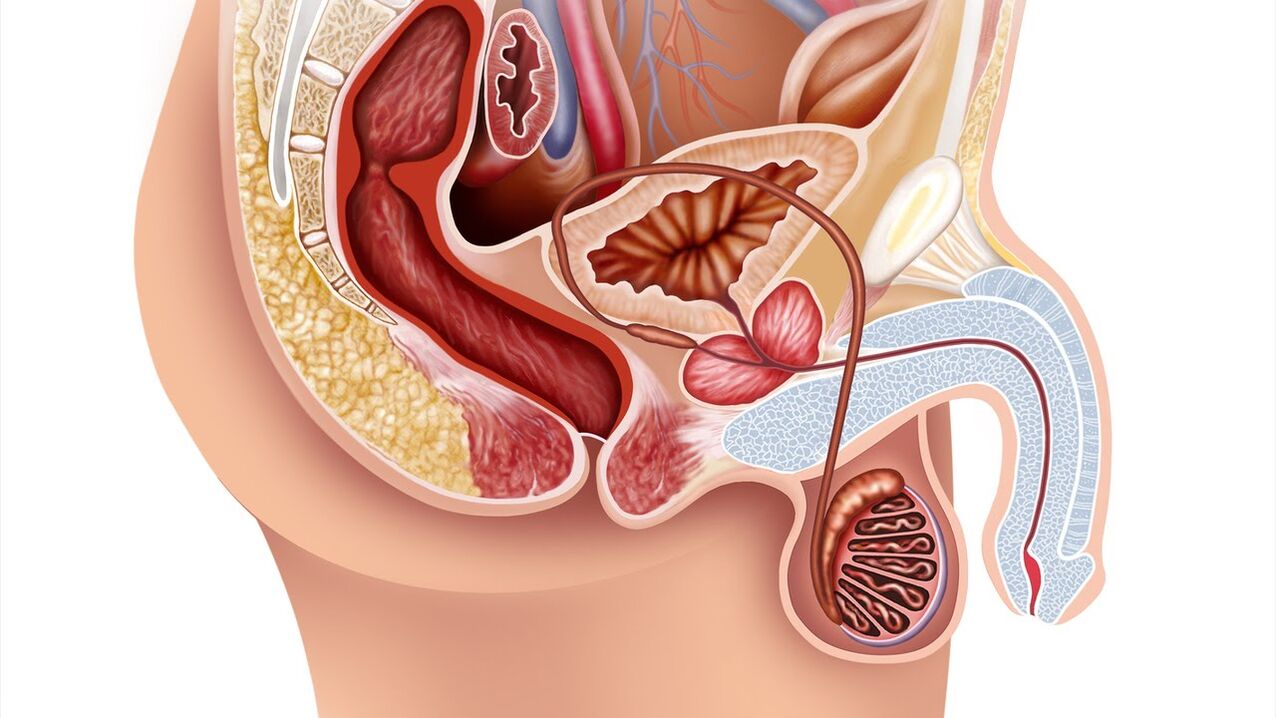
The prostate is the male reproductive system. Shaped like a chestnut, it is located in front of the rectum, below the bladder, and surrounds the urethra (urethra). When the prostate becomes inflamed, it can compress the urethra, which can lead to further problems with urination. The main function of the prostate is to produce a secret (fluid) that is part of semen and dilute it, thus ensuring normal sperm motility.
Prostatitis is very common in the practice of urologists. It can occur suddenly or gradually, continuously and over a long period of time (chronic prostatitis). The chronic form of the disease is more common than the acute form. Chronic prostatitis ranks fifth in the top twenty diagnoses in urology.
Since prostatitis is an active foci of infection in the body, it requires mandatory treatment, even if its symptoms do not bother you.
Causes of prostatitis
The list of causes of prostate inflammation is very diverse:
- Genitourinary diseases (cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis);
- sexually transmitted infections (trichomoniasis, gonorrhea);
- Infections associated with pneumonia, influenza, tonsillitis, boils;
- Chronic constipation, forcing men to work constantly;
- A sedentary lifestyle and irregular sex, leading to secret stagnation;
- Urinary retention - swelling of the bladder can increase pressure on the prostate;
- Frequent hypothermia (or overheating);
- Injuries to the pelvic area;
- Hormonal imbalances that weaken the immune system.
Many times, the appearance of prostatitis is caused by purulent microorganisms: Escherichia coli, Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, Mycoplasma, Candida, Trichomonas, Mycobacterium tuberculosis. They multiply rapidly and destroy prostate tissue, which manifests as inflammation.
In most cases, prostatitis occurs with an infection that enters the prostate through the urethra. It happens to enter the body through the blood or lymph, passing through the bladder or rectum.
important! A weakened immune system is very dangerous for people with chronic prostatitis because the prostate can become rapidly inflamed due to fatigue, stress, lack of sleep, malnutrition and other adverse factors.
Due to a sedentary lifestyle and lack of consistent sex, the blood supply to the pelvic organs deteriorates, leading to hypoxia and hyperemia of the prostate tissue. The secret of stasis is the ideal environment for the development of pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation.
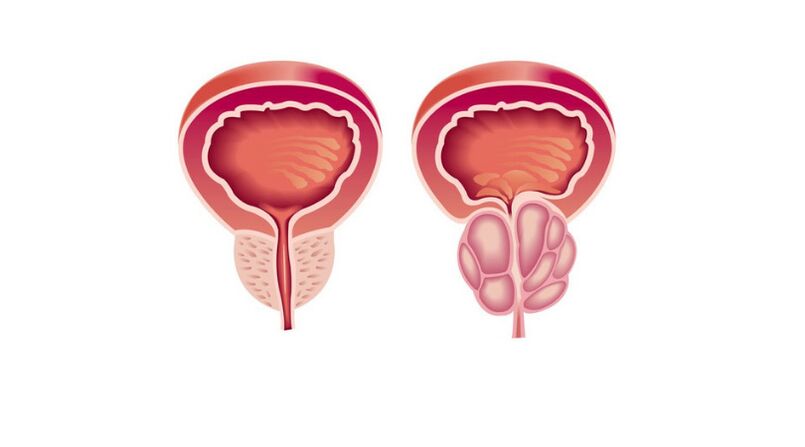
Types and forms of prostatitis
Prostatitis, depending on the cause of the disease, is divided into types and forms:
Distinguish by type:
bacterial prostatitis- Inflammation caused by infection. Bacterial prostatitis occurs in both younger and older men.
congestive prostatitis- Inflammation due to stasis of secretions. It occurs in men with sedentary lifestyles who do not have regular sex. This form can be quickly replenished by infection, and then the stasis process is complicated by the bacterial form.
calculous prostatitis- Stones form in the prostate. Untreated chronic prostatitis can lead to this complication. The disease affects older men who do not follow the advice of urologists.
They are differentiated according to the form of the stream:
acute prostatitis- This is inflammation of the prostate caused by infectious agents, characterized by the appearance of edema and purulent foci in the tissue. 30-58% of men of reproductive age (30-50 years old) face such a diagnosis.
chronic prostatitisCharacterized by persistent or recurrent urogenital symptoms caused by bacterial infection of the prostate. The chronic form accounts for 10% of all prostatitis cases.
symptoms of prostatitis
generalSymptoms of Prostate InflammationYes:
- lower back pain;
- discomfort during bowel movements;
- pain in the perineal or pelvic area;
- Lower urinary tract work disorders.
The acute phase of prostatitis is accompanied by systemic toxic syndrome. The disease is characterized by prominent symptoms and vivid clinical manifestations:
- A sharp rise in body temperature, chills, nausea, vomiting, and malaise;
- joint and muscle pain syndrome and chills;
- Enlarged prostate gland and discomfort in the perineal area;
- Frequent urination and urinary retention.
In the context of an individual inflammatory process, a form of purulent sepsis affecting the blood may appear. In this case, the patient must be hospitalized urgently: with sepsis, the treatment of prostatitis should be carried out only in the clinic.
existbacterial chronic prostatitisUsually there are no symptoms, so treatment is only started when a urinary tract infection is detected, which manifests itself in the context of complications of the disease. In this case, you might observe:
- pain during ejaculation;
- blood in the ejaculate;
- discharge from the urethra;
- Erectile dysfunction may occur.
If the examination does not show that the chronic pain is caused by a prostate lesion, then in this case we are dealing withchronic nonbacterial prostatitisor so calledchronic pelvic pain syndromeA man's quality of life is greatly reduced with this disorder, as it can lead to various psychological and sexual ailments:
- increased fatigue;
- a feeling of helplessness;
- erectile dysfunction;
- painful ejaculation;
- Pain after sex, etc.
Similar symptoms may apply to other urinary disorders, so symptoms alone cannot diagnose prostatitis. For example, prostate adenoma, cystitis, various tumors of urogenital organs, etc. all have urination disturbance and pain.
Diagnosis of prostate inflammation
After identifying the first signs of an inflammatory process in the prostate, the patient should immediately contact a doctor-urologist. Doctors must rule out many diseases with similar presentations and determine which disease it belongs to.
To confirm that the patient does not have other diseases (eg appendicitis, oncology, inflammatory processes of the bladder and kidneys, prostate adenoma), the doctor must perform the necessary tests:
- medical record collection (asking patients);
- ordinary inspection;
- rectal examination;
- Research the secrets of the prostate;
- Sexually transmitted infection analysis;
- Ultrasonography of the prostate, scrotum, and pelvic organs.
At the appointment, the urologist should explain to the patient the duration of the clinical manifestations of the disease, the location and nature of pain (eg, perineum, scrotum, penis, and inner thighs), and characteristic changes in sperm (presence of pus and blood).
Doctors determine the diagnosis of chronic bacterial prostatitis, with symptoms lasting at least three months.
The investigation will include:
- A digital rectal examination of the gland is performed to determine the extent of prostate enlargement and its consistency.
- Analysis of prostate secretions, urine and/or ejaculate.
- Identification of urogenital infections.
- Urodynamic studies.
- Ultrasonography of the urinary system (kidneys, prostate, bladder, and determination of residual urine).
- Culture of prostatic secretions and microscopic examination of parts of urine and prostatic secretions.
- Androflor is a comprehensive study of the male genitourinary tract microbial community by PCR that will determine the qualitative and quantitative composition of the microbial community.
After identifying the cause, your doctor will recommend a course of treatment. It must be remembered that standard methods can detect infection, which eventually leads to prostatitis, in only 5-10% of cases.
Patients must receive a thorough diagnosis, as the success of treatment will depend on the accuracy of the results.
treat prostatitis
When a urologist makes a diagnosis, determining the cause and form of prostatitis, he must prescribe treatment.
The leading role in the treatment of this disease is assigned to drug therapy:
Antibacterial treatment
In the first stage of treatment, it is necessary to eliminate inflammation. Antibiotics are the main treatment for acute bacterial prostatitis and are recommended for chronic bacterial prostatitis. Doctors choose antibacterial drugs based on the bacteria that cause the disease. Patients will have to take oral antibiotics for 4-6 weeks in a course. Chronic or recurrent prostatitis takes longer to resolve. Hospitalization may be required for very severe manifestations, where a course of intravenous antibiotics will be given. Usually, this occurs in acute bacterial prostatitis.
Treatment with alpha1-blockers
When urinating is difficult, doctors prescribe alpha-1 blockers, which help promote urination and relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder. Muscle relaxants will relieve pain caused by a swollen prostate, which can put pressure on adjacent muscles. NSAIDs will help relieve pain syndrome.
In addition, doctors may prescribe auxiliary drugs: biostimulants, extracts of various plants and insects, in the form of rectal suppositories. Unfortunately, medication alone is still insufficient for the treatment of prostatitis.
In the treatment of this disease, the principle of the order of action must be observed. The treatment of prostatitis is always complicated.
Physiotherapy for Prostatitis
In the chronic prostatitis category, you can also use physical therapy:
- massage the prostate (prostate);
- Laser Treatment;
- Microwave hyperthermia and hyperthermia;
- Electrical stimulation with modulated current with skin or rectal electrodes;
- Acupuncture (acupuncture).
Alternative methods, such as leech therapy (treatment with medical leeches), are sometimes used to treat prostatitis, but the effectiveness and safety of this method have not been proven.
Introduction to Stem Cells
Cell therapy (stem cell injection) is a promising treatment for prostatitis today, and it is in the early stages of development. Regarding the injection of stem cells into the prostate, only hypotheses can be made about its mechanism and empirical data obtained by individual research groups.
Surgical treatment of prostatitis
Surgical methods are used to treat complications of prostatitis (seminal vesicle abscesses and suppuration).
Treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome requires separate consideration. Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis does not require treatment.
Prostatitis diet and lifestyle
Prostatitis does not require a special diet, but eating more vegetables, lean meat, and dairy products can help improve bowel function. It is necessary to enrich your body with adequate amounts of fiber, foods rich in vitamin E (wheat germ, corn oil, etc. ) and replace sugar with natural honey. Proper nutrition and prostate inflammation will help improve bowel function and reduce the likelihood of recurrence or speed recovery. Patients need to limit themselves to coffee, stop drinking alcohol, drink plenty of water, and stick to a healthy lifestyle.
Preventive measures to prevent prostatitis
When a person lives the right way of life: he follows proper nutrition, participates in sports, then his chances of developing chronic prostatitis are very small. Rejecting bad habits and casual sex is the way to prevent this disease.
important! There is primary and secondary prevention to prevent the development of prostatitis in men.
basic- Aims to prevent the occurrence of diseases. It all boils down to maintaining a balanced diet, physical activity, timely treatment of any infectious diseases in the body, and regular protective intercourse.
middle school- Aims to prevent recurrence of existing chronic prostatitis and provides regular checkups by a urologist and preventive treatment with multivitamins, restorative medicines and exercise.